Cryogenic Temperature Monitoring
If you are looking for a cryogenic temperature monitoring that helps you and your team eliminate manual logging, improve compliance readiness, and protect all your temperature-sensitive assets, you’ve arrived at the right place.

Let us help you evaluate your needs!
- Safety: Alerts via text, email, push notifications and phone calls to protect your precious assets
- Compliance: Automated compliance reports
- Efficiency: Reduced Manual Logging and time spent on reports
And what makes us different?
- Lifetime Warranty: Never buy hardware again!
- Unlimited Users: Scale across your entire organization
- Connectivity Flexibility: Wi-Fi, Cellular or Data Hub
- Phone call alarms: Alerts won't get ignored
- Mobile App: 500 Freezers in your pocket
- Facility monitoring: Simple to add water leak, door open, occupancy, and even IAQ monitoring
Engineered in Indiana with U.S.-based support.
Healthcare Monitoring
From the operating room to the cafeteria freezer, risks of a broken freezer or compromised clean room can range from the loss of tens of thousands of dollars in inventory to adverse patient outcomes.
Healthcare Brochure
See What Customers Say About Sonicu
Asset Protection. Compliance Automation. And Reduced Manual Processes.
Sonicu serves thousands of professionals at hundreds of organizations across North America by improving how they monitor and manage their most sensitive assets and environments.
Professionals from healthcare, life science, laboratory and cold chain facility management turn to Sonicu to help them improve the way they do business.



Cryogenic Temperature Monitoring
Some of the finest names in healthcare, including Indiana University Health, University of Michigan Health System, and Stanford University rely on Sonicu to provide a robust and continuous environmental monitoring system, including temperature, humidity, air pressure, and more.
These respected healthcare and research brands turn to Sonicu for four primary reasons:
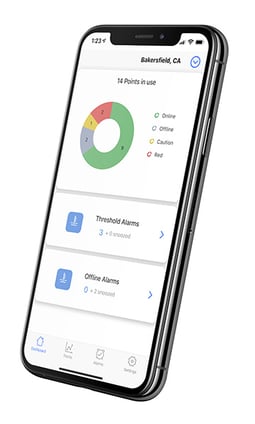
- Real-Time Monitoring: the sensors collect temperature, humidity, air pressure data, and more, and transmit it wirelessly to SoniCloud - our cloud-based platform.
- Operational Efficiency: Virtually eliminate the need for tedious and costly manual logging
- Compliance Automation: Respond to any regulatory audit or inspection in a few clicks with our reports section
- Asset Protection: Detect and respond to any threshold that can threaten anything perishable: food, drugs, vaccines, research, etc.
Our customers stay with us thanks to our American-based customer support, which is never more than a phone call away. While our technology is intuitive and powerful, we know it’s only as strong as the people who stand behind it.
Cryogenic temperature monitoring refers to the precise measurement and control of extremely low temperatures, typically below -150°C (-238°F).
This specialized field of temperature measurement is crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of materials, processes, and equipment operating at ultra-low temperatures.
Cryogenic monitoring systems employ advanced sensors and sophisticated control mechanisms to ensure accurate and reliable temperature readings in environments where even slight variations can have significant consequences.
The importance of cryogenic temperature monitoring cannot be overstated in industries and applications that rely on extreme cold. Accurate monitoring ensures:
- Safety of personnel and equipment: Preventing accidents related to rapid temperature changes or equipment failure.
- Preservation of sensitive materials: Maintain the integrity of biological samples, superconductors, and other temperature-sensitive substances.
- Efficiency of cryogenic processes: Optimize energy consumption and process performance in industrial applications.
- Compliance with regulatory standards: Meet strict guidelines in industries such as healthcare and aerospace.
- Prevention of costly failures or product loss: Avoid financial losses due to equipment malfunction or material degradation.
The critical nature of cryogenic temperature monitoring extends beyond mere measurement; it encompasses a holistic approach to managing and controlling ultra-low temperature environments, ensuring the success and safety of various scientific and industrial endeavors.
Sonicu monitoring solutions meet the high demands of clinical, university, laboratory and Contract Research Organization facilities.
Digital sensors and probes, including Sonicu’s first-to-market digital cryogenic and ultra-low temperature probes, are accurate to research tolerances and provide constant protection for valuable assets.
Applications of Cryogenic Temperatures in Various Industries
Cryogenic temperatures find applications across numerous sectors:
- Superconductivity research: Enabling the study of materials with zero electrical resistance.
- Quantum computing: Maintaining the delicate quantum states necessary for advanced computation.
- Particle physics experiments: Cooling superconducting magnets in particle accelerators.
- Food preservation: Flash-freezing to maintain food quality and extend shelf life.
- Cryosurgery in medicine: Precisely destroying diseased tissue while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy cells.
Each of these applications relies heavily on accurate and reliable cryogenic temperature monitoring to ensure optimal performance and safety.
In healthcare, cryogenic temperature monitoring is vital for:
- Preserving biological samples: Maintaining the viability of stem cells, embryos, and other sensitive biological materials.
- Storing vaccines and blood products: Ensuring the efficacy and safety of temperature-sensitive medical supplies.
- Cryosurgery procedures: Precisely controlling the temperature for targeted tissue destruction in cancer treatment and other surgical applications.
- Manufacturing pharmaceuticals: Maintaining specific temperatures during the production and storage of certain medications.
Advanced cryogenic monitoring systems in healthcare often incorporate redundant sensors, automated alarms, and continuous data logging to ensure the integrity of irreplaceable biological materials and critical medical supplies.
Large-scale cryogenic storage facilities rely on precise temperature monitoring for:
- Long-term preservation of genetic material: Maintaining seed banks, animal genetic resources, and human reproductive material.
- Storage of liquefied natural gas (LNG): Ensuring safe and efficient storage of natural gas at approximately -162°C (-260°F).
- Maintaining food quality in cold storage: Preserving the taste, texture, and nutritional value of frozen foods.
These facilities often employ multi-tiered monitoring systems, combining local sensors with centralized control systems and remote monitoring capabilities to manage vast quantities of cryogenically stored materials.

Challenges in Monitoring Cryogenic Temperatures
Monitoring temperatures in cryogenic environments presents a unique set of challenges that pushes the boundaries of measurement technology. The extreme sensitivity required at these ultra-low temperatures is perhaps the most significant hurdle.
Even minute temperature fluctuations can have profound effects on experiments or processes, necessitating detection capabilities that far exceed those of conventional temperature monitoring systems.
Monitoring cryogenic temperatures presents unique challenges:
- Extreme sensitivity requirements: Detecting minute temperature changes that can have significant impacts on experiments or processes.
- Non-linear behavior of sensors at ultra-low temperatures: Compensating for sensor characteristics that change dramatically as temperatures approach absolute zero.
- Potential for measurement drift over time: Ensuring long-term stability and accuracy of sensors in harsh cryogenic environments.
- Need for specialized calibration techniques: Developing and maintaining calibration standards for temperatures far below those encountered in typical industrial processes.
Overcoming these challenges often requires a combination of advanced sensor technologies, sophisticated signal processing algorithms, and rigorous calibration protocols.
Remote Monitoring Solutions
Modern cryogenic systems often incorporate remote monitoring capabilities:
- Wireless sensor networks: Deploying interconnected sensors throughout cryogenic facilities for comprehensive monitoring.
- Cloud-based data storage and analysis: Enabling real-time access to temperature data from anywhere in the world.
- Mobile applications for real-time alerts: Notifying operators instantly of any temperature anomalies or system issues.
Remote monitoring solutions enhance system reliability and operator responsiveness, crucial for maintaining the integrity of cryogenic processes and stored materials.
Integration with IoT for Real-Time Monitoring
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing cryogenic temperature monitoring:
- Continuous data streaming: Providing a constant flow of temperature information for real-time analysis and control.
- Predictive maintenance algorithms: Using AI and machine learning to anticipate potential system failures before they occur.
- Automated control systems: Implementing closed-loop control systems that automatically adjust cryogenic processes based on real-time temperature data.
- Integration with facility management platforms: Incorporating cryogenic monitoring into broader facility management systems for holistic operational oversight.
IoT integration not only improves the accuracy and reliability of cryogenic temperature monitoring but also enables more efficient and responsive management of cryogenic systems.
Benefits of Efficient Cryogenic Temperature Monitoring
Efficient cryogenic temperature monitoring yields a multitude of benefits that extend far beyond mere temperature control. At the forefront of these advantages is the assurance of safety in environments where ultra-low temperatures pose significant risks.
By enabling the early detection of temperature anomalies, robust monitoring systems serve as a critical line of defense against potential hazards.
This proactive approach allows operators to identify and address issues before they escalate into dangerous situations, thereby preventing equipment failures that could result in catastrophic releases of cryogenic fluids or system implosions.
In industries where cryogenic fluids are routinely handled, such as in LNG processing or aerospace applications, the ability to quickly detect and respond to leaks is paramount in preventing personnel exposure and mitigating environmental damage.
Moreover, effective cryogenic monitoring plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with stringent safety regulations that govern industries dealing with extreme low temperatures.
By providing accurate, real-time temperature data, these systems enable facilities to meet or exceed industry safety standards, fostering a culture of safety and regulatory adherence.
This not only protects personnel and assets but also shields organizations from potential legal and financial repercussions associated with safety breaches.
The benefits of efficient monitoring extend well into the realm of operational efficiency.
Precision temperature control, enabled by advanced monitoring systems, leads to optimized energy consumption in cryogenic processes.
By maintaining temperatures at their ideal set points with minimal fluctuations, these systems minimize the energy required to sustain cryogenic conditions, resulting in significant cost savings over time.
This level of control also translates to reduced product waste, as temperature excursions that could compromise the quality or viability of stored materials are effectively prevented.
In many cryogenic applications, particularly those involving the storage of biological samples or the maintenance of superconducting states, even minor temperature deviations can lead to irreversible damage or loss.
Efficient monitoring safeguards these often priceless or irreplaceable materials, ensuring their long-term viability and protecting substantial investments in research and development.
For industries such as biotechnology and quantum computing, where the integrity of cryogenically stored materials is paramount, the value of reliable temperature monitoring cannot be overstated.
Streamlined processes and workflows are another significant benefit of advanced cryogenic monitoring systems.
By automating temperature monitoring and control, these systems reduce the need for manual intervention, minimizing human error and freeing up personnel for more value-added tasks.
The integration of monitoring data with broader facility management systems enables a more holistic approach to operations, whereby cryogenic processes are optimized in concert with other facility functions for maximum efficiency.
Furthermore, consistent temperature management through efficient monitoring contributes to enhanced equipment longevity.
Cryogenic equipment is often subject to extreme thermal stress, and fluctuations in temperature can accelerate wear and tear.
By maintaining stable temperatures and minimizing thermal cycling, monitoring systems help extend the operational life of expensive cryogenic equipment, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
In the realm of scientific research and development, the benefits of efficient cryogenic monitoring are particularly profound.
Precise temperature control enables researchers to conduct experiments with unprecedented accuracy, leading to more reliable results and potentially groundbreaking discoveries.
In fields such as quantum physics and materials science, where behaviors at ultra-low temperatures are of critical interest, the ability to maintain and accurately measure cryogenic conditions is often the key to unlocking new scientific insights.
Best Practices for Cryogenic Temperature Monitoring
Implementing best practices in cryogenic temperature monitoring is essential for maximizing the benefits and reliability of these critical systems. At the heart of these practices is a rigorous approach to sensor calibration and maintenance.
Regular calibration checks are paramount, involving periodic comparisons against known temperature standards to ensure continued accuracy.
This process is particularly crucial in cryogenic applications, where even small measurement errors can have significant consequences.
Calibration procedures should be meticulously documented, creating a traceable history that can be analyzed for long-term trends and used to predict future calibration needs.
Maintenance of cryogenic sensors extends beyond calibration to include regular cleaning and inspection.
In the harsh environments typical of cryogenic applications, sensors can be subject to contamination or physical damage that may affect their performance.
Establishing a routine for sensor cleaning and visual inspection helps identify potential issues before they impact measurement accuracy.
This proactive approach should also include a strategy for the timely replacement of degraded components, ensuring that the monitoring system remains in optimal condition at all times.
Selecting the right equipment for specific cryogenic monitoring needs is another critical best practice.
This process involves a careful evaluation of the temperature range requirements for the application, ensuring that chosen sensors are capable of accurate measurements across the entire range of expected temperatures.
The response time of sensors is another crucial consideration, particularly in applications where rapid temperature changes need to be detected quickly.
Compatibility with existing systems and infrastructure should also be assessed to ensure seamless integration and avoid costly retrofitting or system conflicts.
When choosing monitoring equipment, durability and longevity in cryogenic environments should be key considerations.
Sensors and associated hardware must be designed to withstand not only extreme cold but also other challenging conditions such as vibration, electromagnetic interference, or exposure to cryogenic fluids.
Investing in high-quality, purpose-built cryogenic monitoring equipment often proves more cost-effective in the long run, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing system downtime.
Effective data logging and analysis practices are fundamental to leveraging the full potential of cryogenic monitoring systems.
Implementing robust data logging systems that capture and store temperature data at appropriate intervals is crucial for both short-term control and long-term analysis.
The frequency of data logging should be tailored to the specific needs of the application, balancing the need for detailed information against data storage and processing constraints.
Regular analysis of logged temperature data can reveal valuable insights into system performance and potential areas for optimization.
By identifying patterns or gradual changes in temperature profiles, operators can preemptively address developing issues or fine-tune processes for improved efficiency.
Advanced analytics techniques, including machine learning algorithms, can be employed to translate raw temperature data into actionable operational improvements.
Integrating cryogenic temperature data into broader facility management systems represents a best practice that is gaining increasing importance.
By incorporating cryogenic monitoring into comprehensive data management platforms, organizations can gain a more holistic view of their operations.
This integration enables more sophisticated analysis, where cryogenic temperature data can be correlated with other operational parameters to uncover complex relationships and optimization opportunities.
Training and education form another crucial component of best practices in cryogenic temperature monitoring.
Ensuring that personnel are well-versed in the principles of cryogenic monitoring, the specific equipment in use, and proper safety protocols is essential for safe and effective operations.
Regular training sessions, coupled with clear standard operating procedures, help maintain a high level of competency among staff and promote a culture of safety and precision in cryogenic operations.
Lastly, staying abreast of technological advancements in the field of cryogenic monitoring is a best practice that can yield significant benefits.
The rapid pace of innovation in sensor technologies, data analytics, and control systems means that there are continually emerging opportunities to enhance monitoring capabilities.
Regularly evaluating new technologies and their potential applications can help organizations maintain a competitive edge and continually improve the safety, efficiency, and effectiveness of their cryogenic operations.
Summing Up the Importance of Cryogenic Temperature Monitoring
Cryogenic temperature monitoring plays a pivotal role in advancing scientific research, ensuring product quality, and maintaining safety in various industries.
As we've explored, the challenges of measuring and controlling these extreme temperatures are matched by the critical importance of doing so accurately and reliably.
From healthcare to aerospace, from quantum computing to energy storage, the ability to precisely monitor and control cryogenic temperatures underpins many of the most exciting and important technological advancements of our time.
The sophisticated sensors, advanced monitoring systems, and data analysis techniques employed in this field not only safeguard valuable materials and ensure process efficiency but also push the boundaries of what's possible in science and industry.
The field of cryogenic temperature monitoring continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and the expanding applications of ultra-low temperatures.
As industries push the boundaries of what's possible at these extreme conditions, the demand for more precise, reliable, and integrated monitoring solutions will only grow.
Looking ahead, we can anticipate several exciting developments:
- Further miniaturization of sensors, enabling more granular and less intrusive monitoring
- Integration of artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance and autonomous system optimization
- Development of new materials and techniques for even lower temperature achievements and measurements
- Expanded use of cryogenics in emerging fields such as quantum technologies and advanced materials science
As these advancements unfold, the importance of robust, accurate, and intelligent cryogenic temperature monitoring systems will only increase, cementing their role as a cornerstone of cutting-edge science and industry.
FAQs
What is cryogenic temperature monitoring used for?
Cryogenic temperature monitoring is used in various applications, including preserving biological samples, maintaining superconducting states, storing liquefied gases, and conducting advanced scientific research. It ensures the safety, efficiency, and integrity of processes involving extremely low temperatures.
How accurate are cryogenic temperature sensors?
The accuracy of cryogenic temperature sensors can vary depending on the technology used. High-precision sensors can achieve accuracies of ±0.01°C or better. However, the extreme conditions of cryogenic environments present unique challenges, and regular calibration is essential to maintain accuracy.
What industries benefit most from cryogenic monitoring?
Industries that benefit significantly from cryogenic monitoring include healthcare and medical research, aerospace, energy (particularly LNG storage and transport), food preservation, and advanced scientific research fields such as particle physics and quantum computing.
Can cryogenic temperature sensors be used in extreme environments?
Yes, cryogenic temperature sensors are specifically designed to function in extreme low-temperature environments. However, they must be carefully selected and implemented to withstand not only the cold but also other environmental factors such as mechanical stress, radiation, or magnetic fields, depending on the specific application.
What are the maintenance requirements for cryogenic temperature systems?
Maintenance of cryogenic temperature systems typically involves regular calibration of sensors, inspection of all components for wear or damage, cleaning of sensors and probes, and periodic replacement of consumable parts. Additionally, the entire system should undergo scheduled performance checks to ensure reliability and accuracy.

American-based Customer Support: Robust & Reliable High Touch Service
Software and technology is only as good as the people who stand behind it.
At Sonicu, that means our team of American-based customer success managers who are never more than a phone call away to help field and fix any service issues.
Our probes and sensors are placed in demanding frozen environments and our software literally sends billions bits of data monthly, meaning there’s always the potential for a hiccup on either the hardware or software.
We are committed to fielding every customer service request promptly and addressing our customer’s concerns promptly and professionally.
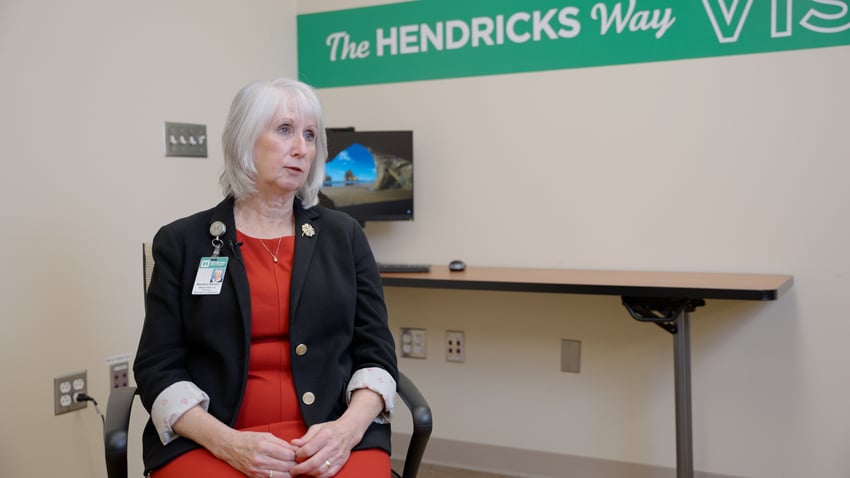
 “I like to say that every refrigerator or freezer is like a car in that they all behave a bit differently,
“I like to say that every refrigerator or freezer is like a car in that they all behave a bit differently,
and then every now and then you just get a bad boy who doesn’t want to perform as we need it to,”
Martha Rardin, Director, Nutrition and Dietetics, Hendricks Regional Hospital.
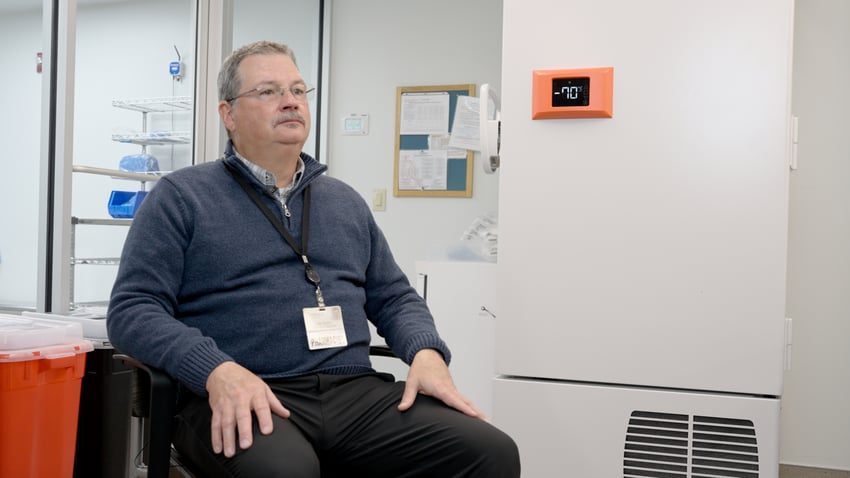 “Sonicu has been a powerful tool to identify which units are behaving out of spec and get our team
“Sonicu has been a powerful tool to identify which units are behaving out of spec and get our team
to fix them before we have a serious issue.”
Tim Livesay, Director, Hancock Regional Hospital Pharmacy Director







How IU Health
consolidated all of its pharmacy monitoring needs
into one cloud-based platform serving dozen of locations.